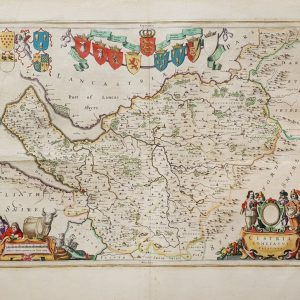
Cheffins’s Map Of The Railways In England And Scotland Accurately Delineating All The Lines At Present Open And Those Which Are In Progress – 1844
Cheffins, Charles Frederick
£75.00
Availability: In stock
Product Description
Cheffins’s Map Of The Railways In England And Scotland Accurately Delineating All The Lines At Present Open And Those Which Are In Progress – Corrected To The Present Time – The Map Also Shows The Main Roads Throughout The Kingdom With The Distances Between The Towns Forming A Complete Guide For The Traveller And Tourist – Fourth Edition – 1844
Publisher: Charles F. Cheffins
Price: £75 including postage in the UK
Publication Date: 1844
Edition: Fourth edition
Map Size: 59cm x 70cm plus western Cornwall
Binding: Original cloth boards with publisher’s paper label
Condition: Very good in very good cloth boards
Condition:
Hand-coloured and engraved folding map, dissected and mounted on linen. Railways in Scotland are shown as an inset with westernmost Cornwall added to the bottom left corner, as issued. Slight marking and foxing. Wear with very minor loss to the fold intersections. Front hinge strengthened. Boards very slightly rubbed. A very good copy in very good binding.
Railways In Britain In The 1840s: A Brief Overview
The 1840s represented one of the most decisive decades in British transport history. What had begun in the 1830s as a promising but limited innovation expanded into a national system that reshaped economic life, social behaviour, and the physical landscape. The period is often described as the era of “Railway Mania”, and with good reason: investment surged, engineering advanced at pace, and railways came to occupy a central role in Victorian Britain.
The Surge of Railway Mania
At the beginning of the 1840s, railways were still relatively new. Yet the commercial success of early main lines led to dramatic speculation. Investors from across society—from aristocrats and industrialists to clerks and shopkeepers—poured money into railway schemes, sometimes with only a hazy understanding of their feasibility.
Parliament, overwhelmed by the volume of proposed lines, authorised thousands of miles of new track. Between 1844 and 1847 especially, railway companies multiplied at a remarkable rate. This speculative enthusiasm was not entirely sustainable, and by the late 1840s the bubble burst, leaving many companies overstretched and many investors disappointed. Nevertheless, the mania resulted in lasting infrastructure that shaped the national network.
Engineering Achievements and Innovations
Despite the financial excesses, the 1840s saw impressive feats of engineering. Several developments during this decade had long-term consequences:
Standard Gauge Takes Hold
A major step towards consistency was the increasing adoption of the standard gauge (4 ft 8½ in), particularly as the broad gauge championed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel struggled to maintain dominance. This shift laid the groundwork for a more unified national network.
Ambitious Construction Projects
Engineers designed and built bold new works—tunnels, viaducts, cuttings and embankments on an unprecedented scale. Early large termini appeared in London and other major cities, setting standards for Victorian railway architecture. Tunnels of exceptional length and complexity, along with more powerful locomotives, made long-distance travel faster and more reliable.
Locomotive Advancements
Steam engines became stronger, more efficient, and more dependable. Improvements in boilers, braking mechanisms, and track quality increased safety and comfort for passengers.
Transformations in Everyday Life
The impact of the railways extended far beyond engineering. They reshaped how Britons lived, worked, and communicated.
Faster and More Accessible Travel
Journeys that once took days by coach could now be completed in hours. Rail travel became increasingly affordable and was no longer the preserve of the wealthy. This mobility helped expand employment opportunities and opened up leisure travel for a wider range of people.
Rise of Standardised Time
Before the 1840s, timekeeping was local and inconsistent. Railways required precise timetabling, leading companies to adopt “railway time”—a uniform standard that eventually led to the nationwide adoption of Greenwich Mean Time.
Boost to Commerce and Industry
Railways connected industrial regions with ports and markets more efficiently than canals or roads. Goods could be transported quickly and cheaply, giving British industry a competitive advantage. The postal system was transformed, enabling much faster communication and supporting the growth of business, journalism and public administration.
Growth of Towns and Urban Networks
Towns with stations flourished. New suburbs emerged along railway lines, especially around London, as commuting became possible for the first time.
Economic Consequences: Boom and Bust
By the late 1840s it was clear that speculation had outpaced reality. Many lines authorised during Railway Mania were expensive or impractical to build, and the financial markets contracted sharply. Numerous investors suffered losses, and several smaller railway companies were forced into consolidation or reorganisation.
However, the long-term story is one of substantial benefit. Much of the infrastructure authorised during the mania eventually formed the backbone of the Victorian railway system. The crisis also prompted improved regulation and more rigorous planning, leading to greater stability in the decades that followed.
A Lasting Legacy
By the end of the 1840s, the United Kingdom possessed one of the most advanced and extensive railway networks in the world. The decade had:
- established rail travel as a normal part of daily life
- set engineering standards for future projects
- fuelled industrial growth
- reshaped patterns of settlement and communication
- provided a model for railway development overseas
In essence, the 1840s were the years in which the British railway system moved from novelty to national necessity—a transformation that helped define the Victorian age and continues to influence the country’s infrastructure today.
Why buy from us?
At Hornseys, we are committed to offering items that meet the highest standards of quality and authenticity. Our collection is meticulously curated to ensure that each item is a valuable and authentic piece of history. Here’s what sets us apart:
- Authenticity and Provenance: Every item is researched, collated, and verified for authenticity.
- Expert Curation: Each item is selected with a keen eye for significance, condition, and rarity, ensuring a collection that is both diverse and distinguished.
- Customer Satisfaction: We strive to provide an exceptional customer experience, from detailed descriptions and provenance to secure and prompt delivery of your purchase.
- Returns Policy: We offer an unconditional guarantee on every item. If you wish to make a return, items may be sent back to us within fourteen days of receipt for any reason. We request advance notification of returns, and items must be returned in the same condition as sent for a full refund.
Explore Our Collection:
Visit Hornseys to explore our fine collection of rare and signed books, maps, artwork and objects. Whether you are an avid collector or looking for a special gift, our selection offers something truly unique. Located in the picturesque Yorkshire Dales, our Ripon gallery has been a haven for book lovers, art enthusiasts, and collectors since 1976.
Thank you for looking.
Related products
Yorkshire: An Accurate Survey Of Some Stupendous Remains Of Roman Antiquity On The Wolds In Yorkshire
£195.00Haynes, John & Vertue, George